Beta Design Consultants provide consulting services related to Flood Risk Assessments to developers and clients professional teams. We have prepared flood risk assessments for some relatively large and complex projects as well as typical residential and commercial/industrial developments.
Our Flood Risk Assessments examine site location, historic rainfall data, forecast for peak rainfall including reasonable allowance for future global warming. The surface area that contributes to flooding, along with any mitigation measures are considered to quantify flood risk.
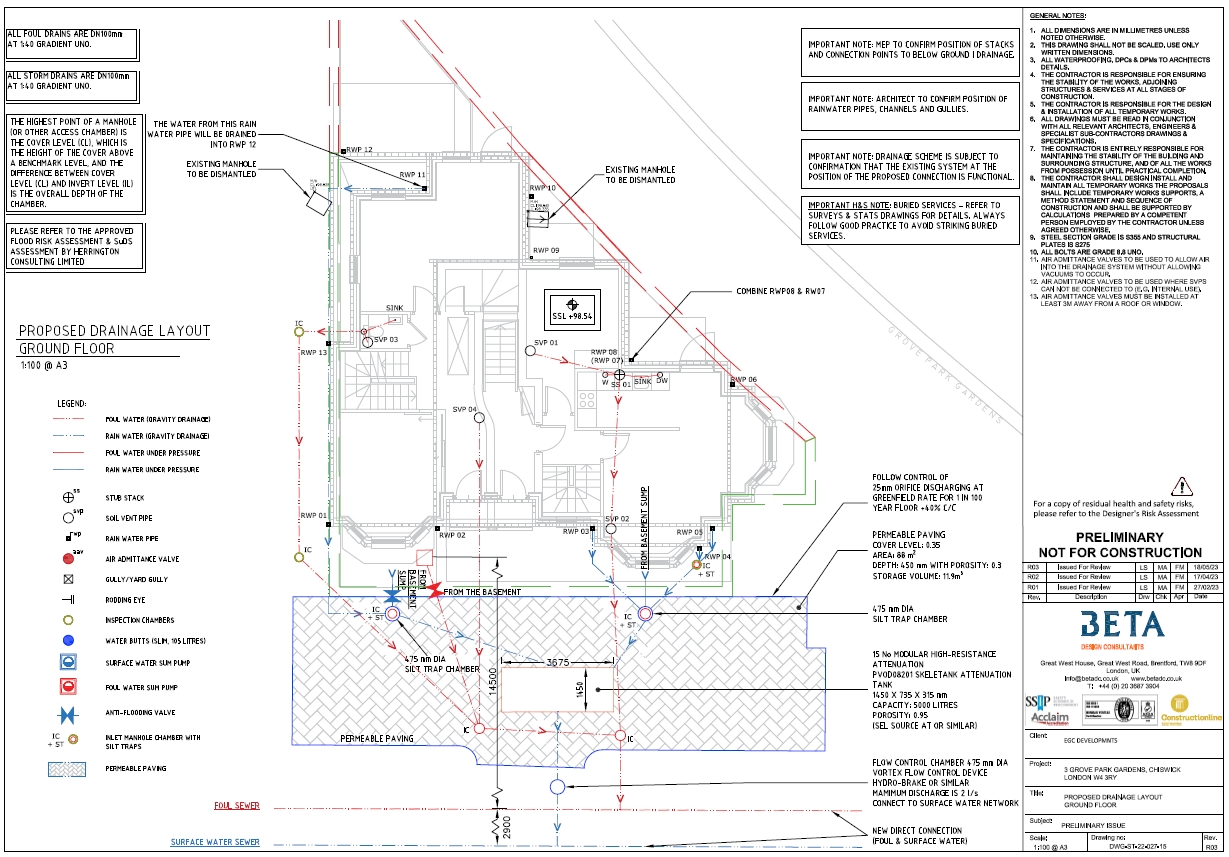
To mitigate flood risks, the surface water drainage study is prepared. Sustainable drainage system SuDS are identified to evaluate opportunities for flood risk mitigation and to offering advice to clients and developers on how the flood risk at peak rainfall can be managed.
Sustainable drainage systems are designed and sized to reduce the volume, frequency and flow rate of surface water runoff and during extreme events. Exceedance can be managed, with components and schemes "failing gracefully" and in many circumstances they can be visually monitored.
SuDS Measures and Techniques
- Greening: for example, in a recent application to increase parking provision in an outer London Borough, we proposed used of grass-crete parking surfacing. This is why in some cases, considerations of transport need to be considered with considerations of flood risk assessment and an integrated multi-disciplinary consulting services such as the one offered by Beta ensures effective communication between project consultants and clear communication of requirements across disciplines. Another option is the use of roof gardens which has become very popular in dense areas.
- Permeable Surfaces: for example a combination of green areas such as grass-crete with permeable paving that allows the water to be locally managed rather than discharging into the national system and potentially contributing to a flood event at the exceedance event.
- Storage: for example the use of water harvesting storage, attenuation tanks or ponds or a combination thereof.
Relevant Case Studies
- Planning Permission for New Provision of Parking in Richmond.
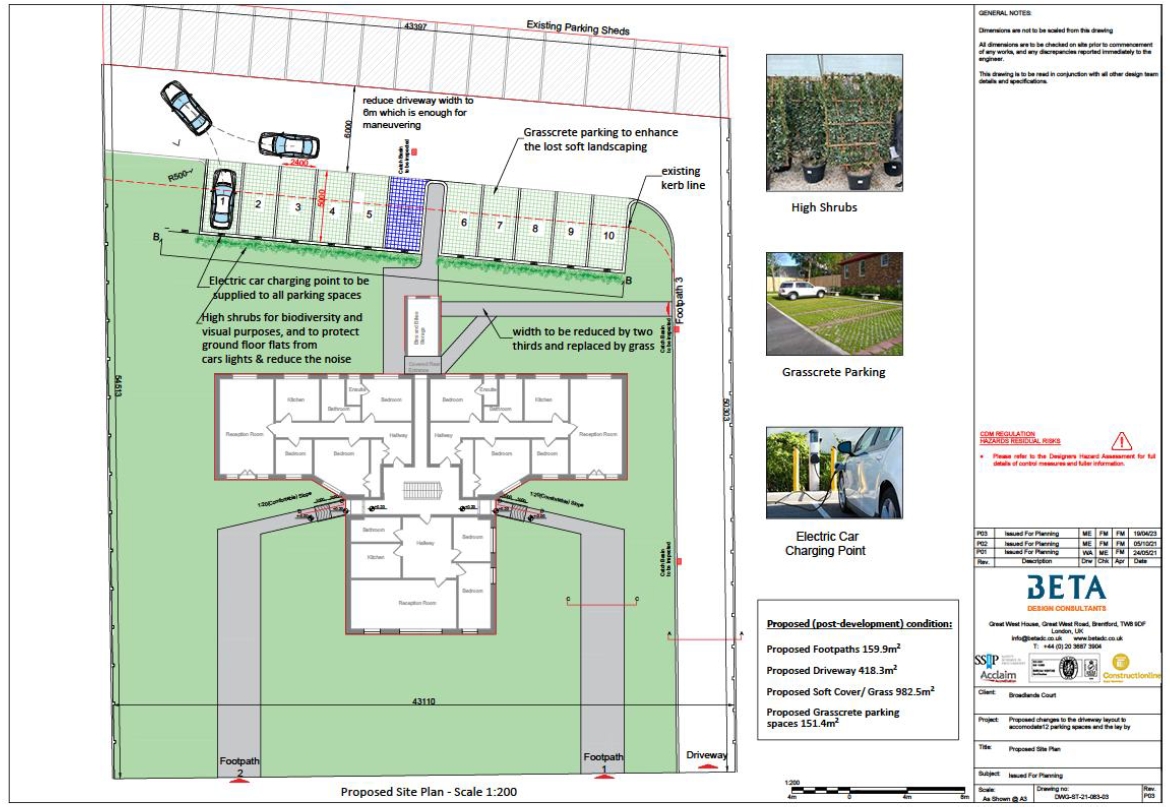
- Residential development use of permeable paving and attenuation.